In today’s digital age, organizations face a multitude of security threats, and while external cyberattacks often dominate the headlines, it is important not to overlook the dangers that lie within. Insider threats, posed by individuals who have authorized access to sensitive information or systems, can be equally devastating. In this article, we will explore what insider threats are, the different types of threats, their motivations, detection and prevention strategies, as well as real-world case studies.
By understanding these risks and implementing effective measures, you can safeguard your organization’s valuable assets from internal threats.
Table of Contents
What Counts as an Insider Threat?
Insider threats can come from employees, contractors, or even vendors who have access to confidential information and systems. They can use their privileged access to steal data, disrupt operations or cause other damage. Motivations run the gambit, from malicious intent to negligence to plain old accidents. Businesses must have the right security measures in place to mitigate these risks and protect their assets from malicious actors.
The best defense against insider threats is a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes robust authentication measures, regular monitoring of user activity, and proactive risk assessment. With the right tools and processes in place, businesses can reduce their exposure to insider threats and protect their valuable resources from unauthorized access.
Insider threats are a major concern for businesses in the digital age. Robust, up-to-date, and continuously monitored cybersecurity is essential to protect against malicious insiders who have access to sensitive data and systems. With the right tools, businesses can detect and respond quickly and effectively.
Types of Insider Threats
Insider threats can be categorized into three main types: malicious insiders, negligent insiders, and compromised insiders.
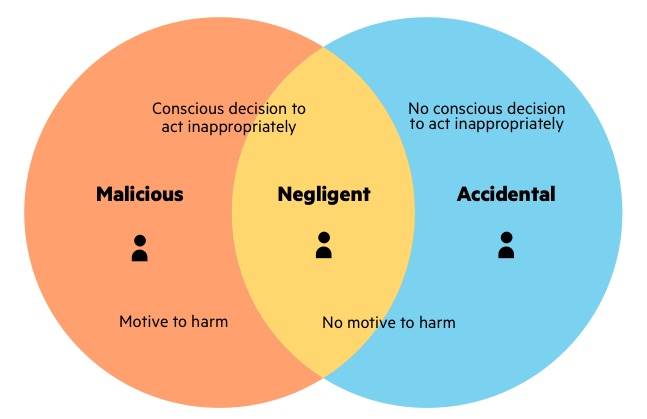
Malicious Insiders
Malicious insiders are individuals who intentionally misuse their access privileges to harm an organization. They may have grievances against the company, seek personal gain, or have ulterior motives. These individuals could be disgruntled employees, former employees seeking revenge, or individuals recruited by external entities to carry out insider attacks.
Negligent Insiders
Negligent insiders, on the other hand, pose a threat unintentionally due to carelessness or lack of awareness. They may unknowingly violate security policies, mishandle sensitive information, or fall victim to social engineering attacks. Negligent insiders can create vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit.
Compromised Insiders
Compromised insiders are individuals whose authorized access has been compromised by external actors. Cybercriminals may use various techniques such as phishing, social engineering, or malware to gain control over an employee’s credentials or device. Once compromised, these insiders unknowingly become conduits for attackers to exploit the organization’s systems and data.
Causes and Motivations
Insider threats can arise from various causes and motivations. Understanding these factors can help organizations identify potential risks and implement appropriate preventive measures.
Disgruntled employees are a common source of insider threats. Employees who feel undervalued, mistreated, or unfairly treated may develop resentment towards their organization, leading them to exploit their access privileges for personal gain or to cause harm.
Financial gain is another significant motivation for insider threats.
Insiders may engage in fraudulent activities, such as embezzlement or insider trading, enriching themselves. Financial pressures or the desire to maintain a lavish lifestyle can drive individuals to exploit their positions.
Revenge or sabotage is another potential motivation for insider threats. Employees who have been terminated, passed over for promotions, or have personal conflicts with colleagues or superiors may seek retaliation by compromising systems, stealing data or spreading damaging information.
Espionage poses a significant threat, especially for organizations dealing with sensitive information or intellectual property. Competitors, foreign governments, or criminal organizations may infiltrate an organization by recruiting insiders to gather classified data, trade secrets, or strategic plans.
Mitigating Insider Threats
Effectively mitigating insider threats requires a multi-layered approach that combines technology, policies, and employee awareness.
Implementing comprehensive employee training and awareness programs is crucial. Employees should be educated about the risks of insider threats, taught to recognize warning signs, and trained on security best practices. By providing regular training sessions, organizations can foster a culture of security consciousness and empower employees to become active participants in detecting and preventing insider threats.
Strict access controls and monitoring mechanisms are essential to limit the potential damage caused by insiders. Implementing a least privilege principle ensures that employees have access only to the information and systems necessary to perform their job responsibilities. Regular monitoring of employee activities, network traffic, and system logs can help identify any anomalous behavior or unauthorized access attempts.
Regular security audits and assessments are vital to proactively identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization’s security posture. By conducting periodic reviews of access privileges, system configurations, and security controls, organizations can identify and address potential insider threat risks before they are exploited.
Implementing robust data loss prevention (DLP); measures is critical for preventing the unauthorized exfiltration of sensitive information. DLP solutions can monitor data movements, detect policy violations, and prevent the unauthorized transfer or sharing of confidential data. This can help organizations protect their intellectual property, customer data, and other sensitive information from insider threats.
Why Should You Be Concerned?
More than one-third of businesses are negatively impacted by insider threats every year. Remember, these can be on purpose or unintentional!
Some of the most common mistakes insiders make include:
- Sharing your password or using a weak one
- Not enforcing privileged access controls
- Failure to use multi-factor authentication
- Downloading infected files or clicking malicious links
Conclusion
Insider threats are a major concern for businesses and organizations when it comes to cybersecurity. It is a type of threat that is difficult to detect because the malicious actor may have legitimate access and be difficult to distinguish from other benign users. Set measures in places that can detect and prevent these types of threats before they cause significant damage!
Insider threats are responsible for 60% of data breaches in companies like yours. YOU can help prevent your personal data, the company’s data, and all the PII of your clients from getting spread on the Dark Web.
Education is prevented! Reading this blog has been a great stride forward in your security awareness and cyber-threat preparedness. Contact T3 Today to Mitigate any Threats!

