Phishing scams are fraudulent attempts by cybercriminals to obtain sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and social security numbers. These scammers typically disguise themselves as trustworthy entities, such as banks, social media platforms, or popular online services, to trick individuals into revealing their personal information.
Table of Contents
Types of Phishing Scams
Email Phishing: This is one of the most common phishing scams, where scammers send deceptive emails appearing to be from legitimate sources.
Smishing: Phishing attacks conducted through SMS or text messages, usually containing links or requests for personal information.
Vishing: Phishing attempts made via phone calls, where scammers pose as legitimate organizations and manipulate individuals into sharing sensitive data.
Spear Phishing: A targeted form of phishing that focuses on specific individuals or organizations, using personalized information to appear more convincing.
Recognizing Phishing Emails
Phishing emails often exhibit certain characteristics that can help you identify them:
- Misspelled words or poor grammar
- Generic greetings instead of personalized ones
- Urgent requests for personal information or immediate action
- Suspicious email addresses or domains
Always be skeptical of emails asking for sensitive information and double-check the sender’s identity before responding or clicking on links.

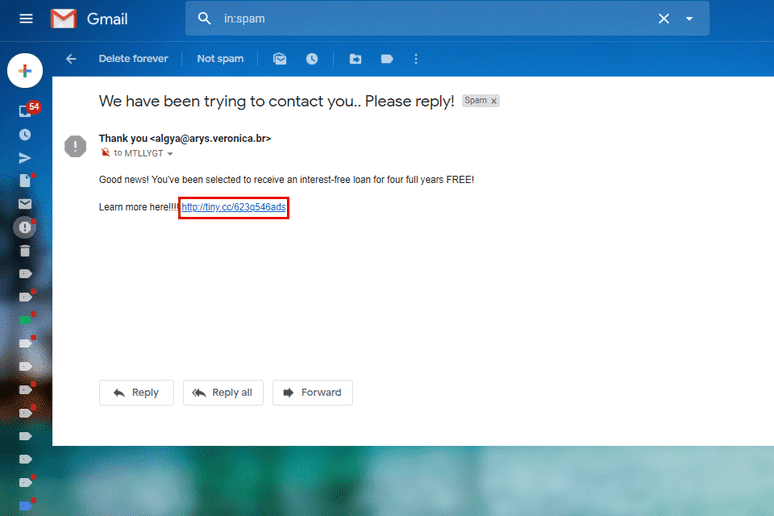
Avoiding Suspicious Links
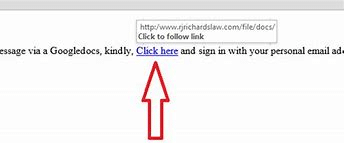
Hover over links: Before clicking on any link, hover your mouse cursor over it to reveal the actual URL. Check if it matches the displayed text, and if it seems suspicious, avoid clicking on it.
Type URLs directly: Instead of relying on links, manually enter the website address into your browser to ensure you are accessing a legitimate site.
Beware of shortened URLs: Shortened links hide the actual destination. Use URL expander services to reveal the full link before clicking.
Strengthening Password Security
Use strong, unique passwords: Create passwords with uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information such as names or birthdates.
Password managers: Consider using password managers to securely store and generate complex passwords for your various accounts.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Utilize 2FA whenever available, as it adds an extra layer of security by requiring a verification code in addition to your password.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Enforcing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection by requiring two different forms of identification before granting access to an account. An email address or trustworthy device will normally receive a password and a special verification code. To safeguard against unwanted access, turn on 2FA for your online accounts.
Verifying Website Security
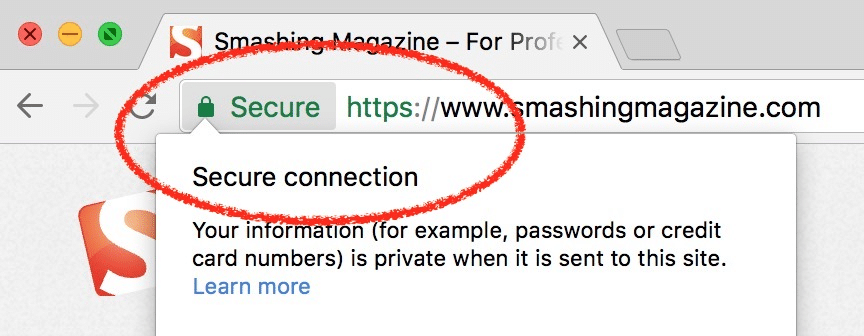
Check for HTTPS: Before submitting any personal information to a website, ensure that the website has a secure connection indicated by “https://” at the beginning of the URL.
Look for a padlock icon: A padlock symbol in the address bar is another indication of a secure website.
Be cautious about sharing information: Avoid entering personal or sensitive information on untrustworthy or unsafe websites.
Secure Wi-Fi Connections
Use encrypted Wi-Fi networks: When connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, ensure they are encrypted, or password protected. Avoid accessing sensitive accounts or making financial transactions on unsecured networks.
Disable automatic Wi-Fi connections: Turn off the option for your device to automatically connect to available Wi-Fi networks, as this can expose you to potential security risks.
Learn more about VPNs to stay protected while surfing on the web!
Keeping Software Updated
Maintaining security requires routinely updating your operating system, web browsers, and antivirus software. Patches that fix flaws and defend against new threats are frequently included in updates. When possible, enable automatic updates to ensure you get the most recent security upgrades.
Educating Yourself and Others
Stay informed about the latest phishing techniques and scams by regularly reading reliable cybersecurity sources. Share your knowledge with friends, family, and colleagues to help them stay protected.
Being Cautious with Personal Information
While giving out personal information over the phone or online, be cautious. Even if they seem legitimate, be wary of unsolicited demands for sensitive information. Keep in mind that reputable businesses almost never call or email you for your personal information.
Regularly Monitoring Your Accounts
Check your internet accounts, credit card bills, and bank statements frequently for any strange activity. Inform the relevant institutions or service providers promptly of any unauthorized charges or account access.
Reporting Phishing Attempts
Report any phishing emails or strange websites you come across to the relevant authorities. Several businesses have specific email addresses or web forms for reporting such events, and most email service providers offer methods to report phishing emails.
Importance of Antivirus Software
Install reputable antivirus software on your devices to protect against malware and phishing attempts. Antivirus programs can detect and block phishing emails, malicious websites, and other potential threats.
Learn more about Antivirus Software with this guide!
Conclusion
Phishing scams are a serious risk to both people and businesses. You can significantly lower your chances of falling prey to these fraudulent schemes by exercising caution and heeding the advice provided in this article. Keep up with current affairs, safeguard your personal information, and immediately report any questionable behavior.
Education is prevented! Reading this blog has been a great stride forward in your security awareness and cyber-threat preparedness. Contact T3 Today to stay protected!

